Turcite® B Slydway® - Technical Data: Typical Properties
| Mechanical Properties | Test Method | Metric | Imperial |
|---|---|---|---|
| Specific Gravity | ASTM D792 | 2.0 - 2.4 | 2.0 - 2.4 |
| Tensile Strength | ASTM D4745 | 13.8 MPa | 2002 psi |
| Tensile Elongation at Break | ASTM D4745 | 100% | 100% |
| Hardness | ASTM D2240 | 50 - 60 Type D | 50 - 60 Type D |
| Peel Strength (Bonded to metal substrate using Waylock® II Adhesive) |
TSS Internal | 178 N /mm | 40 lbf /in |
| Compressive Strength | ASTM D695 | ||
| 0.2% Offset | 7.6 MPa | 1102 psi | |
| 1% Strain | 6.1 MPa | 885 psi | |
| 5% Strain | 13.2 MPa | 1915 psi | |
| Youngs Modulus | 722 MPa | 105 ksi | |
| Deformation Under Load | TSS Internal | ||
| 2 kg/cm2 @ 0.203 mm/min | 0.016 mm | ||
| 4 kg/cm2 @ 0.203 mm/min | 0.030 mm | ||
| 6 kg/cm2 @ 0.203 mm/min | 0.043 mm | ||
| 28 lb/in2 @ 0.008 in/min | 0.0006 in | ||
| 57 lb/in2 @ 0.008 in/min | 0.0012 in | ||
| 85 lb/in2 @ 0.008 in/min | 0.0017 in | ||
| Thermal Properties | |||
| Coefficient of Linear Thermal Expansion | ASTM E831 | ||
| 25°C to 100°C | 103.5 µm/m°C | ||
| 100°C to 150°C | 135.7 µm/m°C | ||
| 77°F to 212°F | 57.5 µin/in°F | ||
| 212°F to 302°F | 75.4 µin/in°F | ||
| Thermal Conductivity | TCi Thermal Analyzer | ||
| 23°C | 0.36 W/m-k | ||
| 73.4°F | 0.36 W/m-k | ||
| Tribological Properties | |||
| Wear Factor, K: Lubricated, Tonna V68 Way Oil | TSS Internal | 3.57 E-08 mm3/Nm | 2.47 E-13 in3/lb-in |
| Friction Coeffiecient: Lubricated, Tonna V68 Way Oil | TSS Internal | 0.034 | 0.034 |
| Color Description | |||
| Turquoise bronze |
Turcite B - Physical Properties
| Property | Units | Test Method | Value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tensile Strength | PSI | ASTM D4894 | 2000 min |
| Tensile Elongation | % | ASTM D4894 | 170 min |
| Specific Gravity | - | ASTM D792 | 3.10 |
| Hardness | Shore D | ASTM D2240 | 50-60 |
Coefficient of Friction
-
Testing data from testing completed at Corporate R&D
|
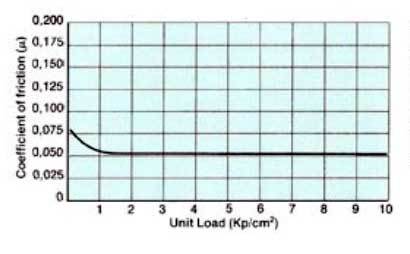
Friction as function of unit load Lubricated friction - Velocity 2 m/min (6,6 ft/min.) Materials: Turcite B (Scraped) Cast iron (Scraped) |
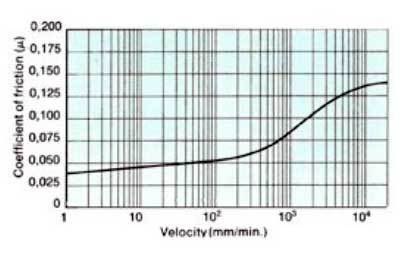
Friction as function of velocity Dry friction - Loading 3.5 Kp/cm2 (50 psi) Materials: Turcite B (Fresh) Cast iron G.S. 55, 264H8, (Ra=0,47) ( 19 CLA) |
 |
 |
|
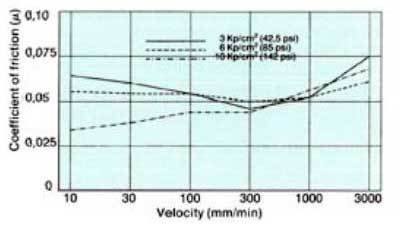
Friction as function of velocity after 0 Krn travel Lubricated with oil 5ºE Materials: Turcite B (Scraped) Cast iron G26 (Ra=0,8) (32 CLA) |
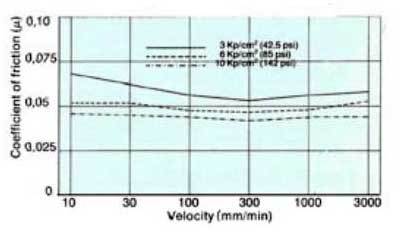
Friction as function of velocity after 40 Km travel Lubricated with oil 5ºE Materials: Turcite B (Scraped) Cast iron G26 (Ra=0,8) (32 CLA) |
 |
 |
-
In the application, Slydway displays only a slight difference between static and dynamic friction, thus eliminating any presence of stick slip.
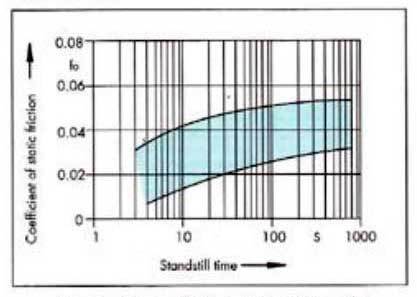
| Figure shows the range of static friction when using different oils. The values were determined on a scraped Turcite®-B sliding surface with a surface contact pressure of 35 N/cm2 and a surface roughness of the guide of Ra=0.6 µ.m. | Figure shows the least differences at the transition to the hydrodynamic range. With higher surface pressures of up to 200 N/m2, the sliding behaviour changes only insignificantly. Good lubrication is of paramount importance in order to achieve a controlled level of dynamic friction. |
 |
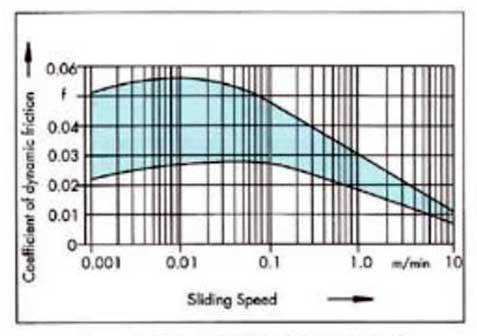 |
| Range of the coefficient of static friction (fp) as a function of the standstill time when using different lubricants. | Range of the coefficient of dynamic friction (f) as a function of the sliding speed when using different lubricants. |
Wear
-
Testing data from testing completed at Corporate R&D
-
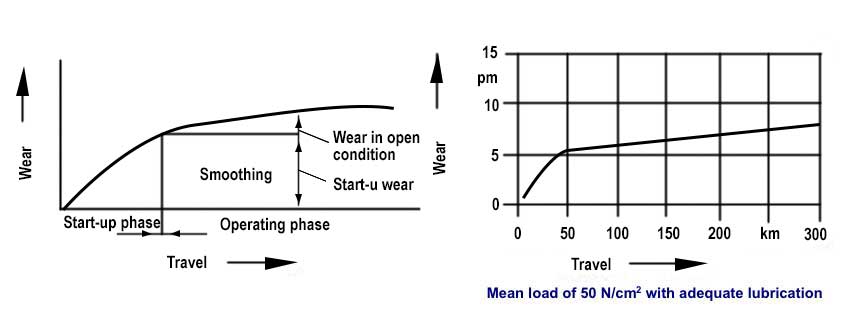
Turcite B Slydway should always be well lubricated during the start-up phase. Very fine particles of the Turcite B Slydway are transferred to the mating surface during the start-up phase.
-
This leads to the slight shading of the metallic mating surface.
-
The start-up phase is concluded with the smoothing phase.
-
-
After the smoothing phase, Turcite B Slydway will experience a low level of both the wear and friction, thus essentially remaining constant.
-
Testing data from testing completed at Corporate R&D
|
Wear as function of travel Lubricated friction - Loading 6Kp/cm2 (85 psi) Materials: Turcite B (Scraped) Cast iron G26 (Ra=0.8) (32 CLA) |
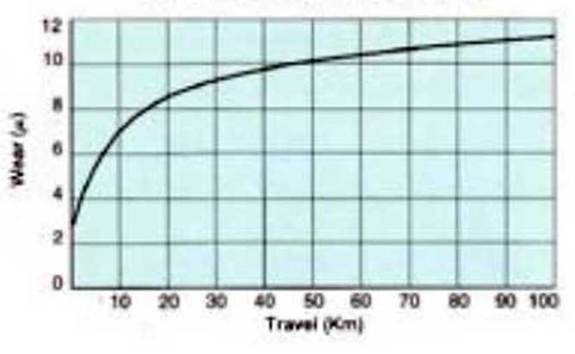
Wear as function of travel Dry friction - Loading 20 Kp/cm2 (284 psi) Materials: Turcite B Steel C60 (Rt=3µ) --------------- Cast iron (Rt = 3µ) _____________ |
 |
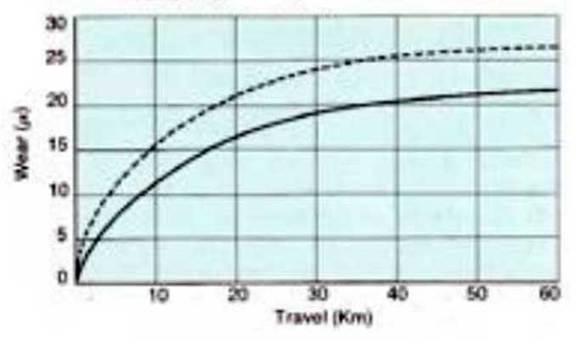 |
Wear - Comparison between Turcite B Slydway & Rulon 142
|
Height of Rulon 142 and Turcite B Samples During Lubricated Test 50psi, WayLube Oil Reciprocating Test but Specimens change Speed and Direction (Velocity) Multiple Times per Cycle |
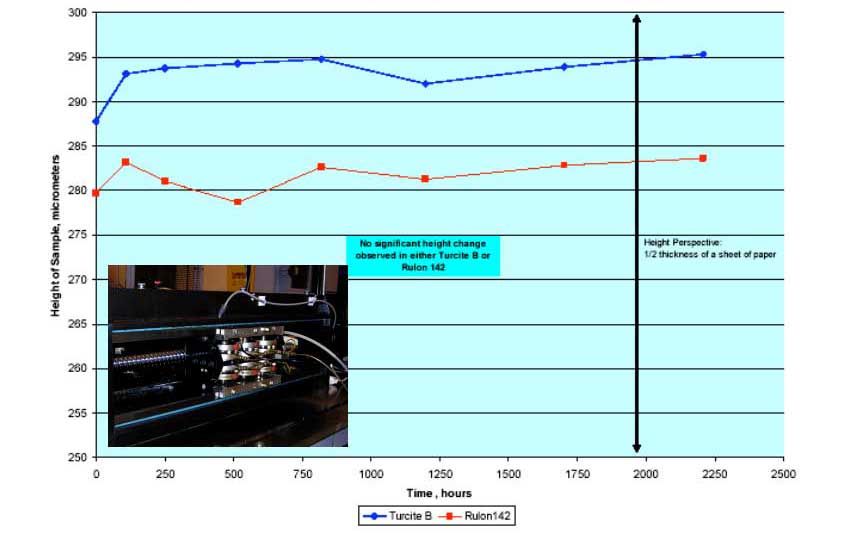 |
Peel Strength Comparison between Turcite B Slydway & Rulon 142
|
Peel Tests on Turcite B Bonded with Waylock II Adhesive, and Rulon 142 bonded with CE211 Material Strip Pulled at 2"/minute |
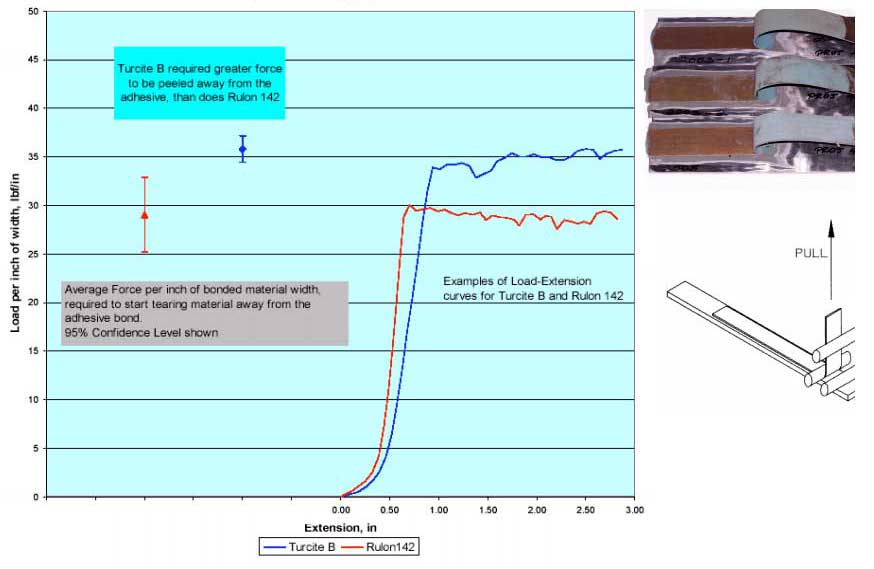 |
For more information on Turcite B, download our Technical Data Sheet.

